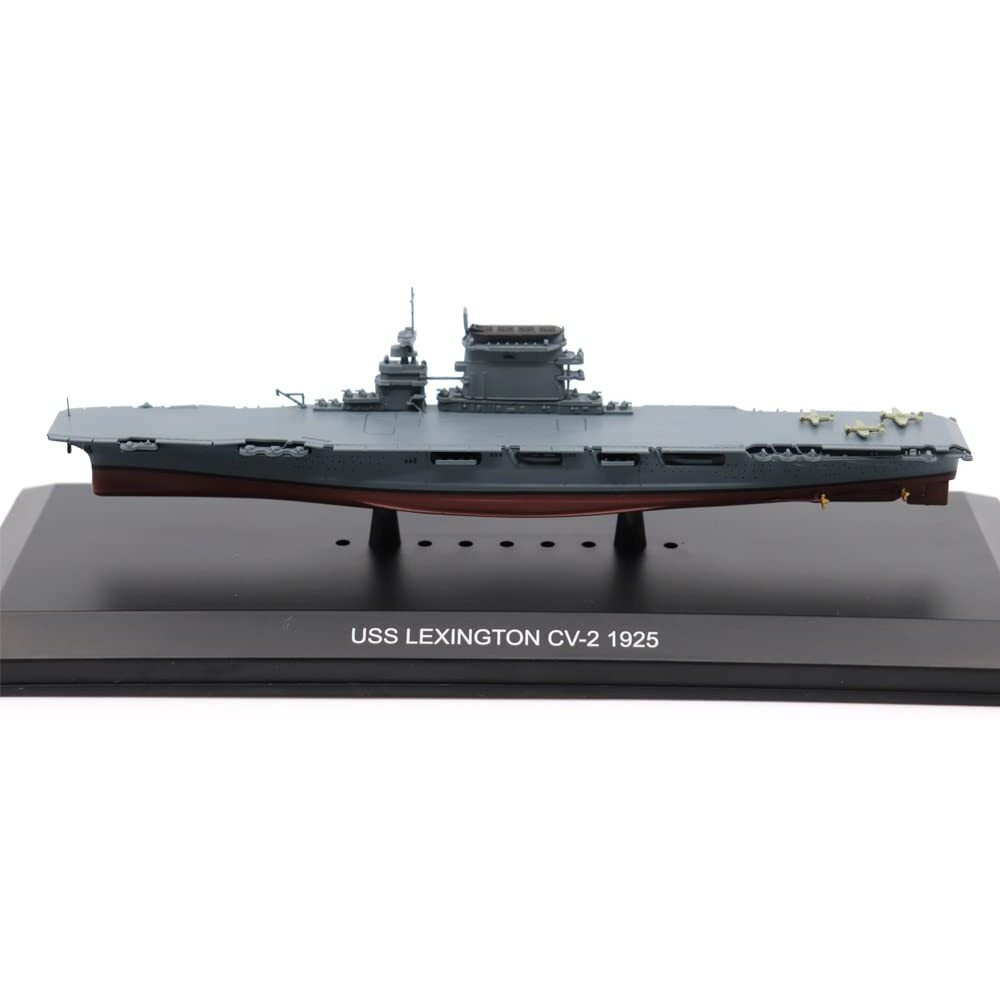
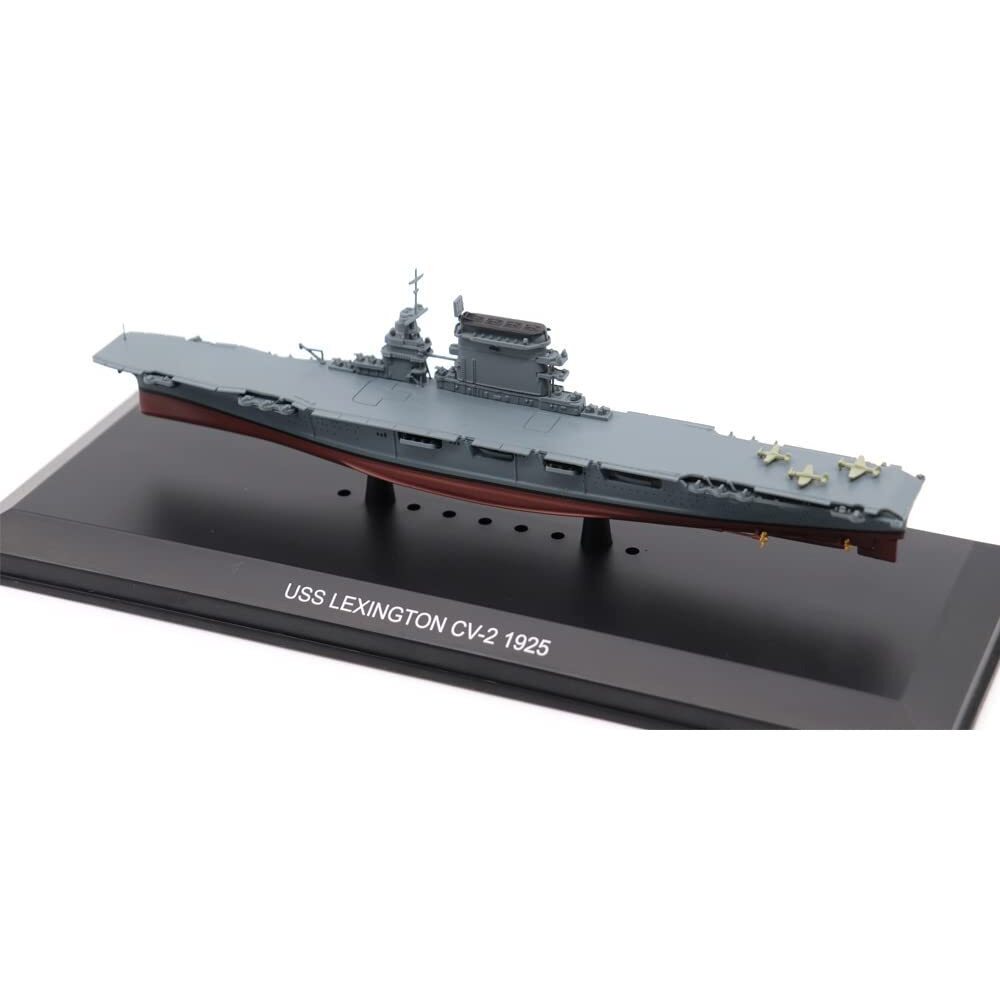
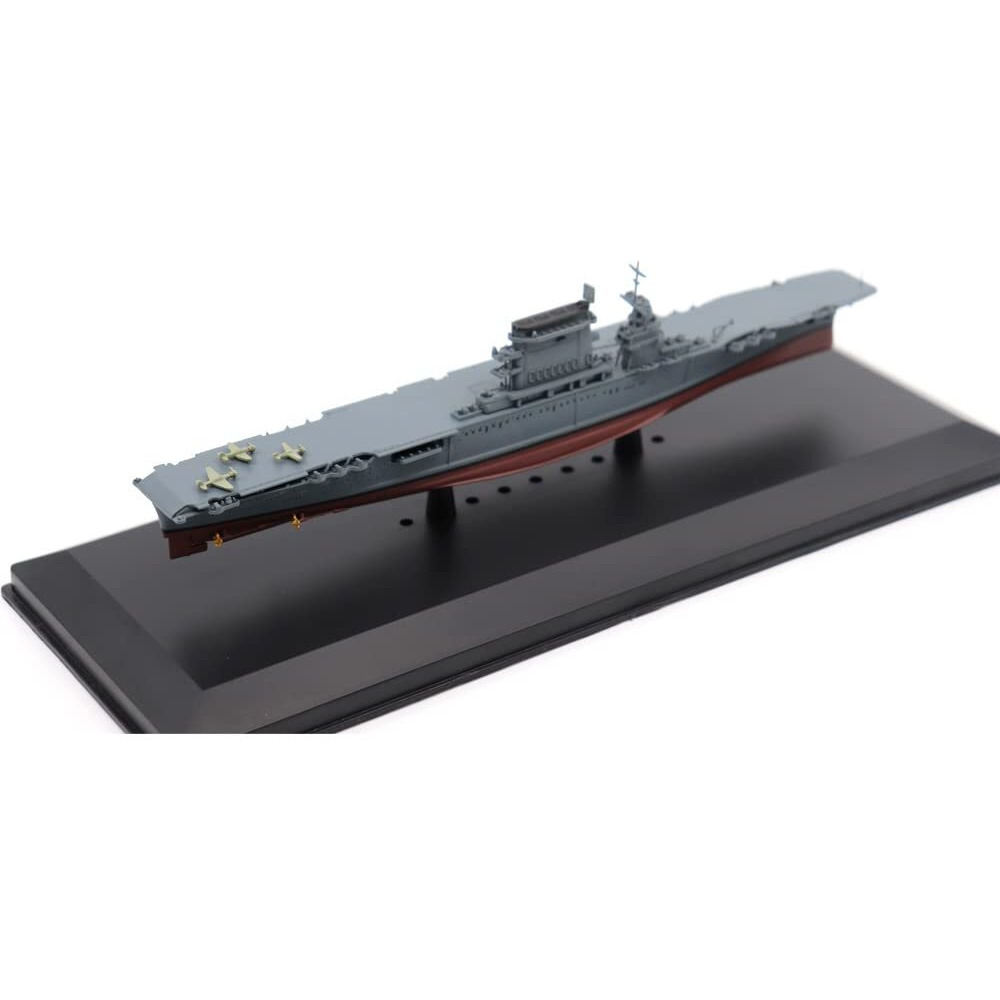
USS Lexington (CV-2), one of the U.S. Navy's first two aircraft carriers, was commissioned in December 1927 at Quincy, Massachusetts. Operating mainly in the Pacific, she took part in fleet maneuvers in the Hawaiian Islands, the Caribbean, and off Panama Canal. When the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, Lexington was transporting aircraft to Midway Island. During the December 11 attempt to relieve Wake Island, which was aborted, she was sent to attack Japanese installations in the Marshall Islands as a diversion. In January and February 1942, her aircraft raided Japanese positions in th southwestern Pacific. Along with USS Yorktown (CV-5) in early May, she participated in the Battle of the Coral Sea. On May 7 and 8, her aircraft took part in the sinking of the Japanese aircraft carrier Shoho and raided the aircraft carriers Shokaku and Zuikaku. The Japanese responded with aircraft attacks, which hit Lexington with two torpedo and three aerial bombs. Following gasoline explosions, she was abandoned and scuttled by USS Phelps (DD-218), leading her to be the first U.S. Navy aircraft carrier lost in World War II. On March 4, 2018, on an expedition to the Coral Sea, the research vessel RV Petrel discovered the remains of Lexington approximately 2 miles under the sea and 430 nautical miles off the coast of Queensland.
Actual product packaging and materials may contain more and/or different information than that shown on our website. We recommend that you do not solely rely on the information presented and that you always read labels, warnings, and directions before using or consuming a product.
For additional information about a product, please contact the manufacturer. Content on this site is for reference purposes and is not intended to substitute for advice given by a physician, pharmacist, or other licensed health-care professional. ZiFiti does not assume liability for inaccuracies or misstatements about products.
Statements regarding dietary supplements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or health condition.